PONA Analysis / Detailed Hydrocarbon Analysis (GC)
PONA analysis is the analysis of hydrocarbon mixtures by separation and quantitation of fractions according to the carbon number or type of hydrocarbon. Analysis can be performed on hydrocarbon types including naphtha, a primary ingredient of petroleum products; gasoline automobile fuel; reformed gasoline (reformate), which is a base ingredient of gasoline, and catalytically cracked gasoline (FCC gasoline).
PONA is an acronym for Paraffins, Olefins, Naphthenes and Aromatics. (called PIONA when distinguishing Isoparaffins from Paraffins)
PONA analyte identification is conducted by matching retention indices with normal hydrocarbon paraffins. Chromatograms obtained in PONA analyses have an extremely large number of peaks and require accurate and reproducible flow control to prevent misidentification. The GC-2030 incorporates an Advanced Flow Controller that enables highly precise flow control and makes it easy to analyze and identify detailed hydrocarbons (DHA).
The analysis of gasoline is shown below.
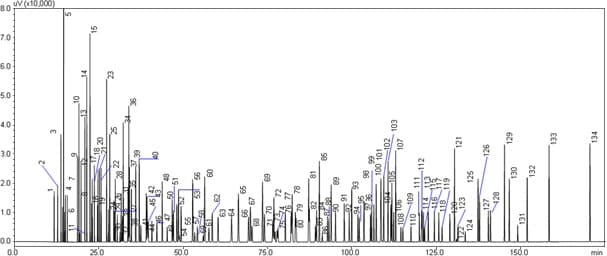
Analysis of Gasoline



